MECHANISM OF ACTION
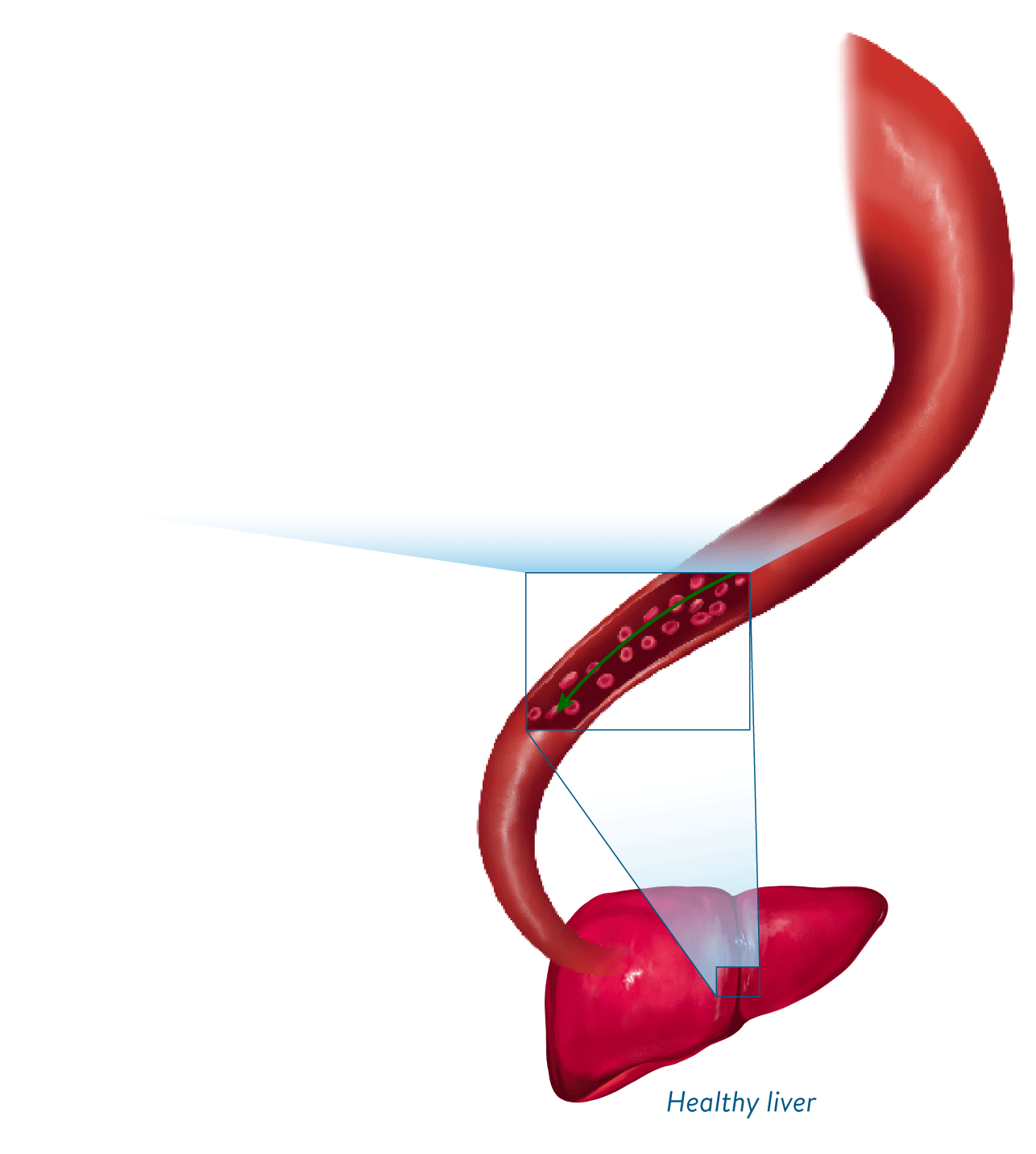
The proposed mechanism of action of Defitelio may help restore blood flow through the liver by acting at multiple points along the VOD progressive cascade1,2
See how Defitelio is thought to work within the VOD cascade
Defitelio protects and stabilizes the vasculature of the liver by restoring endothelial cell homeostasis and thrombotic-fibrinolytic balance, ultimately improving hepatic microvascular circulation1-4,a
aThe mechanism of action of Defitelio has not been fully elucidated.3
aThe mechanism of action of Defitelio has not been fully elucidated.3
aThe mechanism of action of Defitelio has not been fully elucidated.3
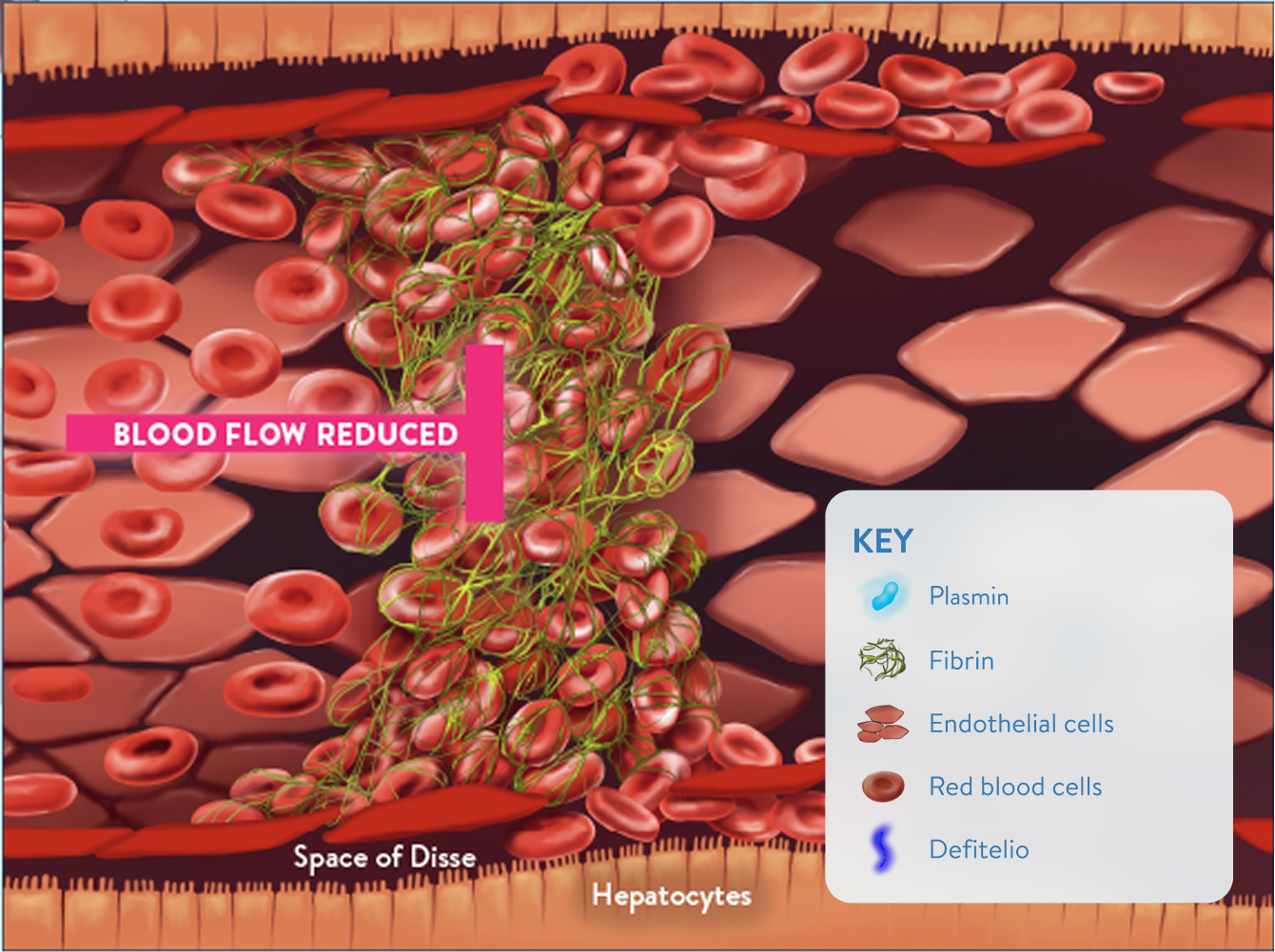
Sinusoidal narrowing and blockage1,2
- Endothelial cell damage
- Red blood cells and debris move into the space of Disse
- Blockage from fibrin deposition, clot formation, and sinusoidal narrowing
- Reduced blood flow
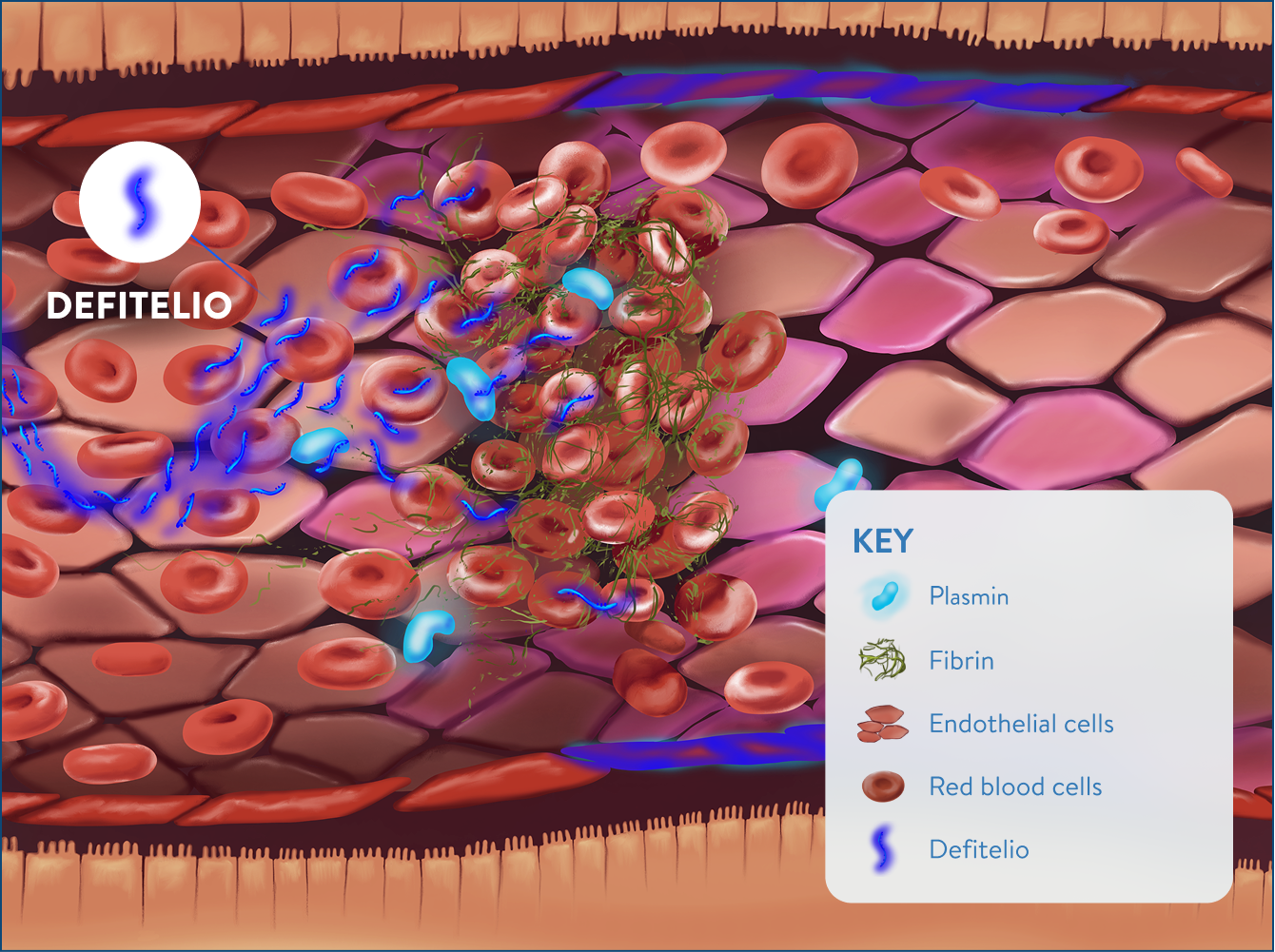
Protection and stabilization with Defitelio3,5
- Increased enzymatic activity of plasmin
- Increased fibrinolysis
- Endothelial cell proliferation
- Partial revascularization
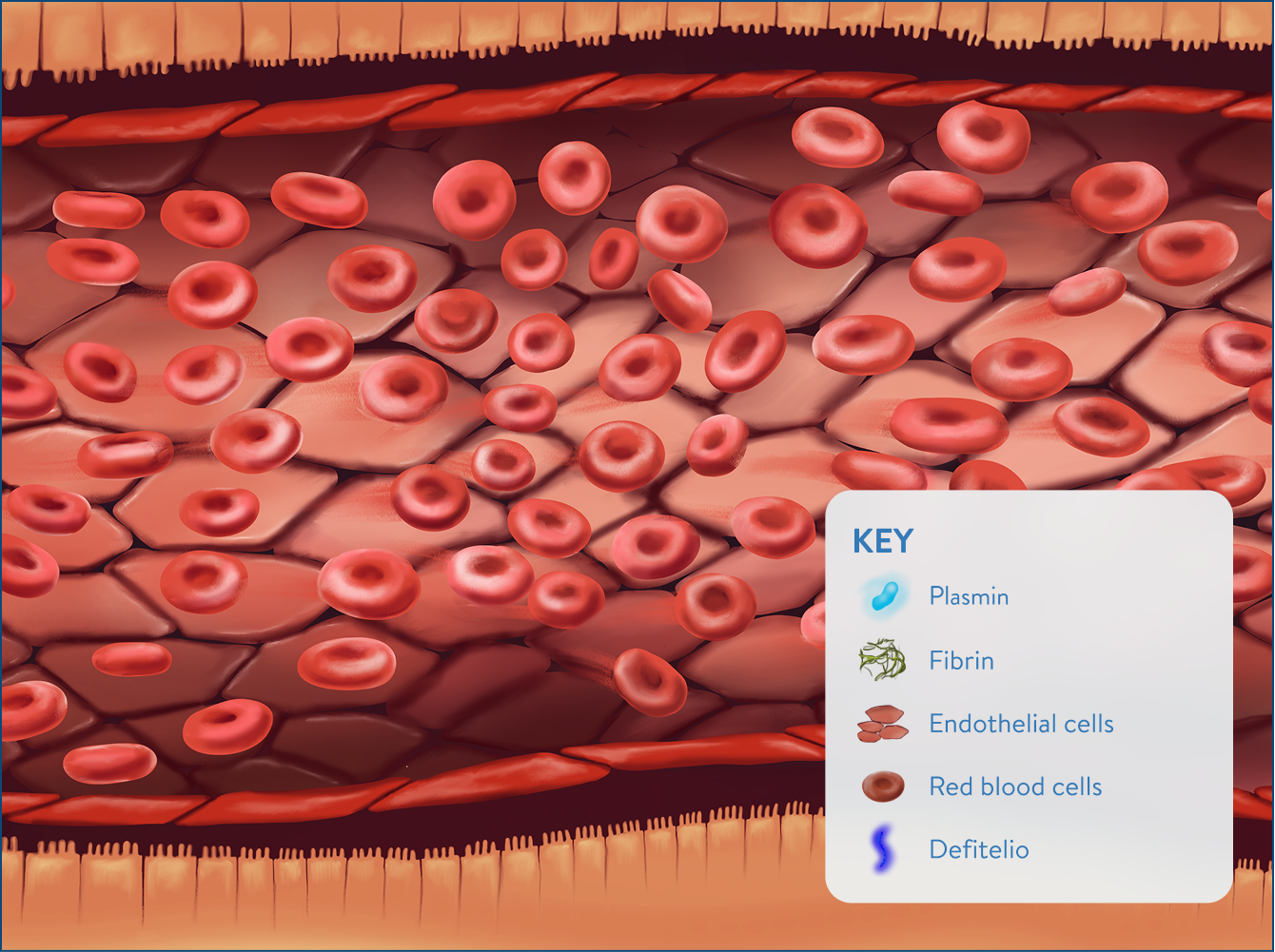
Improved hepatic circulation and restored blood flow through the liver2


Sinusoidal narrowing and blockage1,2
- Endothelial cell damage
- Red blood cells and debris move into the space of Disse
- Blockage from fibrin deposition, clot formation, and sinusoidal narrowing
- Reduced blood flow

Protection and stabilization with Defitelio3,5
- Increased enzymatic activity of plasmin
- Increased fibrinolysis
- Endothelial cell proliferation
- Partial revascularization
Improved hepatic circulation and restored blood flow through the liver2


aThe mechanism of action of Defitelio has not been fully elucidated.3
TABLE B: EFFECTS OF DEFITELIO3,6-9
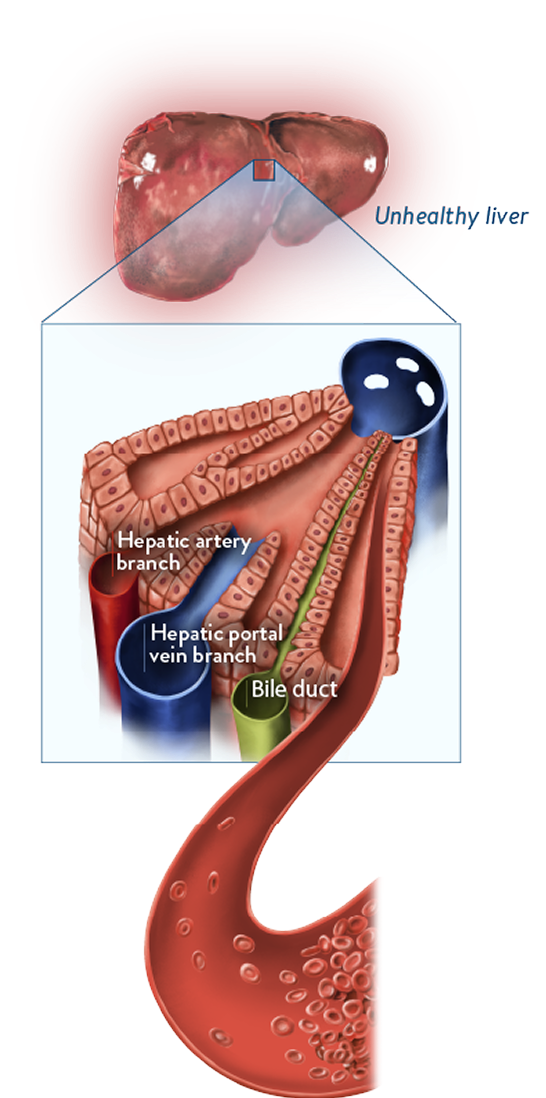
Based on experimental models, buildup of toxic metabolites from HSCT conditioning regimens may trigger activation of and damage to sinusoidal endothelial cells in the liver. This can lead to a cascade of events that is potentially life-threatening.1-4

Endothelial damage
- Activation of endothelial cells triggers expression of cytokines and adhesion molecules, activating inflammatory pathways that cause additional endothelial damage2,3
- Release of the enzyme heparanase contributes to degradation of the extracellular matrix, loss of cytoskeletal structure, and gap formation between sinusoidal endothelial cells1,3
- Degradation of the extracellular matrix leads to detachment of endothelial cells from the sinusoidal lining5,6
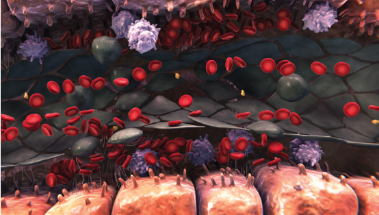
Sinusoidal narrowing
- This ongoing degradation of the endothelium allows red blood cells, leukocytes, and cellular debris to move into the space of Disse1-3
- This can lead to sinusoidal narrowing, which may lead to endothelial cells embolizing downstream and contribute to sinusoidal blockage1-3
References: 1. Carreras E. Early complications after HSCT. In: Apperley J, Carreras E, Gluckman E, et al, eds. The EBMT Handbook. 6th ed. Paris, France: European School of Haematology; 2012:176-195. 2. Richardson PG, Ho VT, Cutler C, et al. Hepatic veno-occlusive disease after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: novel insights to pathogenesis, current status of treatment, and future directions. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2013;19(suppl 1):S88-S90. 3. Richardson PG, Corbacioglu S, Ho VT, et al. Drug safety evaluation of defibrotide. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2013;12(1):123-136. 4. Coppell JA, Richardson PG, Soiffer R, et al. Hepatic veno-occlusive disease following stem cell transplantation: incidence, clinical course, and outcome. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2010;16(2):157-168. 5. Vion AC, Rautou PE, Durand F, et al. Interplay of inflammation and endothelial dysfunction in bone marrow transplantation: focus on hepatic veno-occlusive disease. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2015;41(6):629-643. 6. DeLeve LD, Shulman HM, McDonald GB. Toxic injury to hepatic sinusoids: sinusoidal obstruction syndrome (veno-occlusive disease). Semin Liver Dis. 2002;22(1):27-41.
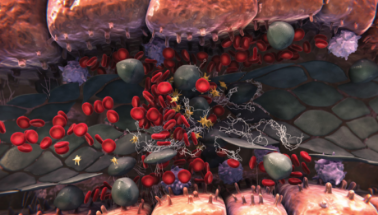
Sinusoidal blockage
- Sinusoidal endothelial cell damage also triggers the expression of multiple factors that regulate coagulation and fibrinolysis1-3
- All of these events can lead to a procoagulant and hypofibrinolytic state, where fibrin deposition, clot formation, and sinusoidal narrowing can cause further blockage1-3
- Hepatocyte cell death is a consequence of sinusoidal disruption, and further sinusoidal obstruction may lead to a reduction in hepatic venous outflow and to postsinusoidal hypertension2-5
References: 1. Coppell JA, Richardson PG, Soiffer R, et al. Hepatic veno-occlusive disease following stem cell transplantation: incidence, clinical course, and outcome. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2010;16(2):157-168. 2. Richardson PG, Ho VT, Cutler C, et al. Hepatic veno-occlusive disease after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: novel insights to pathogenesis, current status of treatment, and future directions. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2013;19(suppl 1):S88-S90. 3. Richardson PG, Corbacioglu S, Ho VT, et al. Drug safety evaluation of defibrotide. Exper Opin Drug Saf. 2013;12(1):123-136. 4. Carreras E. Early complications after HSCT. In: Apperley J, Carreras E, Gluckman E, et al, eds. The EBMT Handbook. 6th ed. Paris, France: European School of Haematology; 2012:176-195. 5. Vion AC, Rautou PE, Durand F, et al. Interplay of inflammation and endothelial dysfunction in bone marrow transplantation: focus on hepatic veno-occlusive disease. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2015;41(6):629-643.